Introduction to the principle, development history and application of 450nm blue lasers
The development of industrial laser technology has always followed the roadmap of production technology and new social requirements. Over the past 60 years, laser technology has made great contributions to solving important tasks in the future of mankind, from digital economy and society, to sustainable energy, to healthy life. Among them, blue-light laser refers to a laser with a wavelength in the range of about 400nm-500nm. Industrial-grade blue-light laser is generally a semiconductor laser.
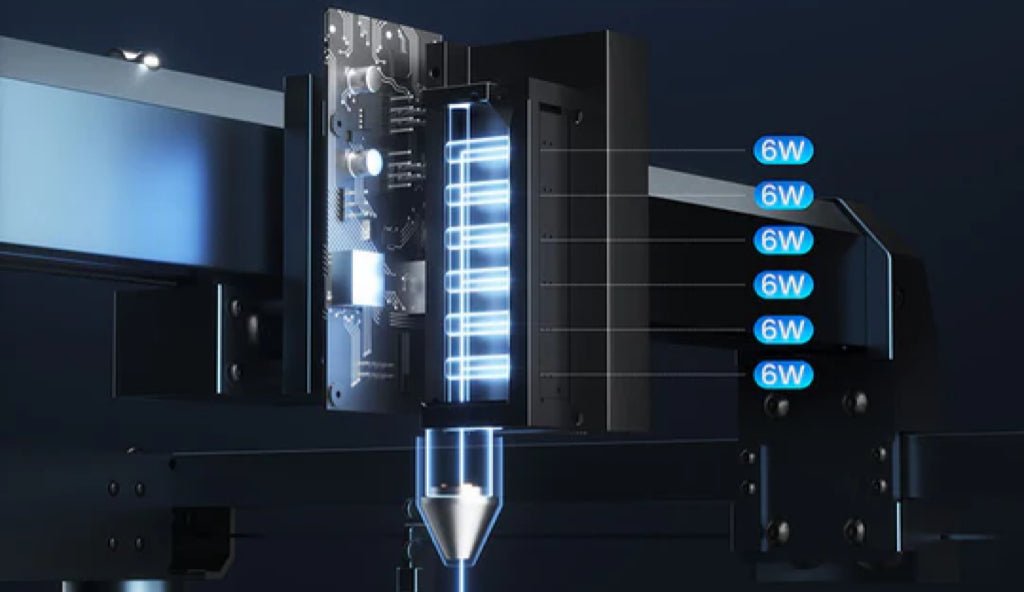
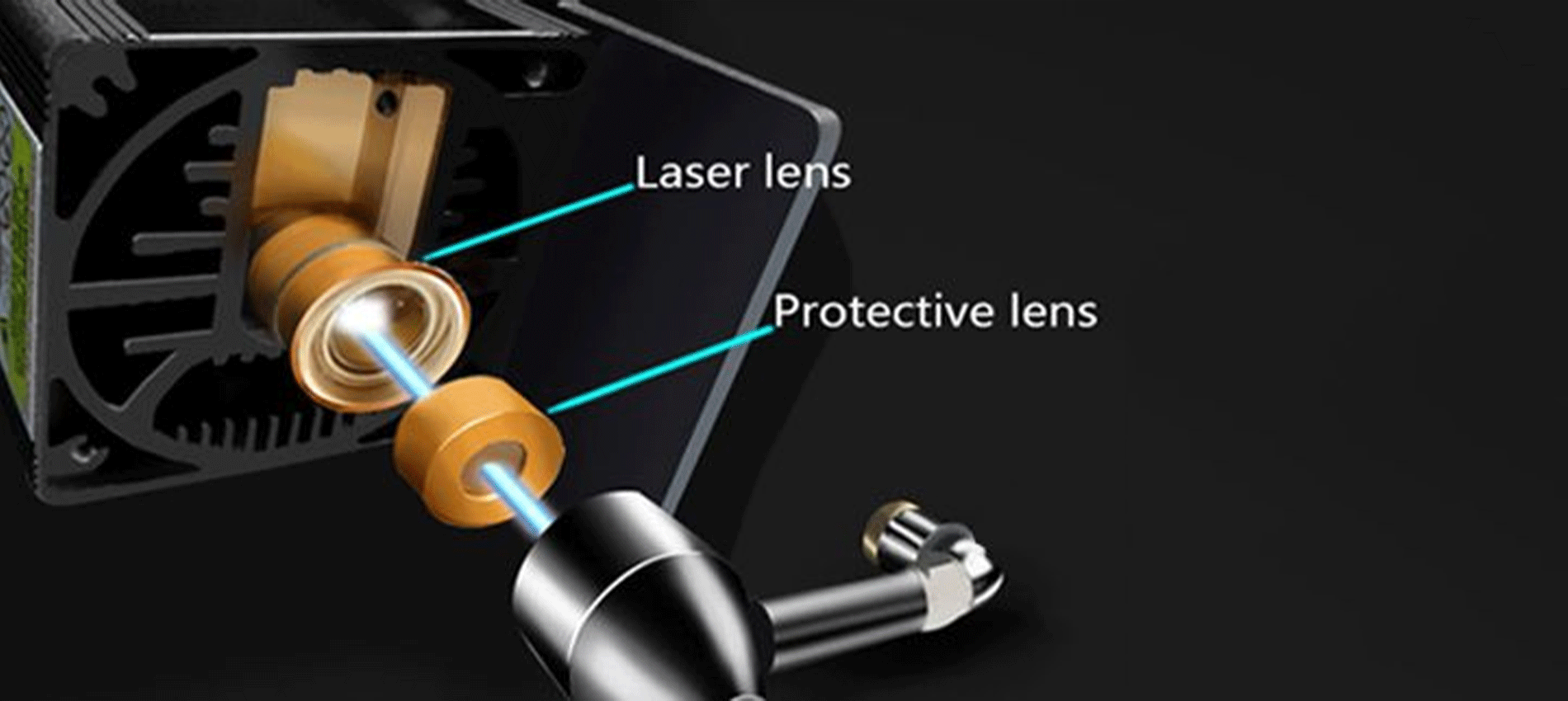
Semiconductor lasers, also known as laser diodes, are lasers that use semiconductor materials as their working material. Semiconductor lasers take electric injection semiconductor lasers as an example. GaN, GaAS and other materials are usually added to the semiconductor material to make a semiconductor junction diode.
When a large enough current is injected into the diode, the electrons (negatively charged) in the middle active region It will spontaneously recombine with holes (positively charged) and release the excess energy in the form of photons, which will then be amplified by multiple reflections in the resonant cavity to form a laser.
Basic structure of semiconductor laser
Among them, in addition to the common characteristics of lasers, semiconductor lasers also have the advantages of small size, low driving power current, high efficiency, long life, easy optoelectronic integration with various optoelectronic devices, and compatibility with semiconductor manufacturing technology for mass production. They are favored by extensive attention and research from various countries. It has become the fastest growing, most widely used, the first to be commercialized out of the laboratory and the largest output value of lasers.
In terms of optical storage optical discs, because the possible recording and reproducing capacity is inversely proportional to the square of the light source wavelength, for example, an optical disc prepared using a 650nm red light semiconductor laser can record 4.7GB, while using 430nm blue light can store 4.7GB. The capacity has been increased to 15GB, so to achieve high density of optical storage, it is necessary to shorten the wavelength of the laser light source. In addition, blue-ray laser has the characteristics of short wavelength, small diffraction effect, and high energy. It has broad application prospects in material processing, optical information storage, display technology, communication technology, laser medical treatment, etc. The radiation wavelength of the semiconductor laser is determined by the bandgap width of the active area material.
Therefore, in order to meet the needs of miniaturization, low power consumption, high reliability and low cost, the use of GaN semiconductor materials has become the best choice for preparing blue lasers.
Therefore, at the 1997 GaN International Conference held in Japan, Nichia announced that the working life of the room-temperature continuous lasing blue laser had exceeded 10,000H. Major companies and powerful universities and research units in the world have invested in research and have successively achieved major achievements. breakthrough. In October 1999, GaN laser was commercialized with output characteristics of 5mW, wavelength of 400nm, operating current of 40mA, operating voltage of 5V, and a lifespan of 10,000h at room temperature, becoming a milestone in the development of GaN. In 2001, Nichia prepared a 150mW laser.
Early bluet lasers were low-power and did not gain much attention. Until recent years, with the marketization of single-tube blue TO packages, prices have been reduced, power has been increased, and various industrial manufacturing and fiber coupling technologies have been continuously enriched. People have realized the feasibility of developing high-power blue lasers.
Nichia NUBM44 Blue Laser Diode
With the winning of the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2014 and the increasing awareness of global environmental protection, GaN light-emitting devices have received widespread attention, especially in the field of lighting. By continuously improving the high brightness and high output of blue light semiconductor devices, blue light semiconductor lasers have entered the era of mass production. But for laser processing, higher power than the blue laser used for these lightings is required. Since blue-light lasers have many advantages as mentioned above, people have been working hard to develop high-power blue-light lasers for laser processing.
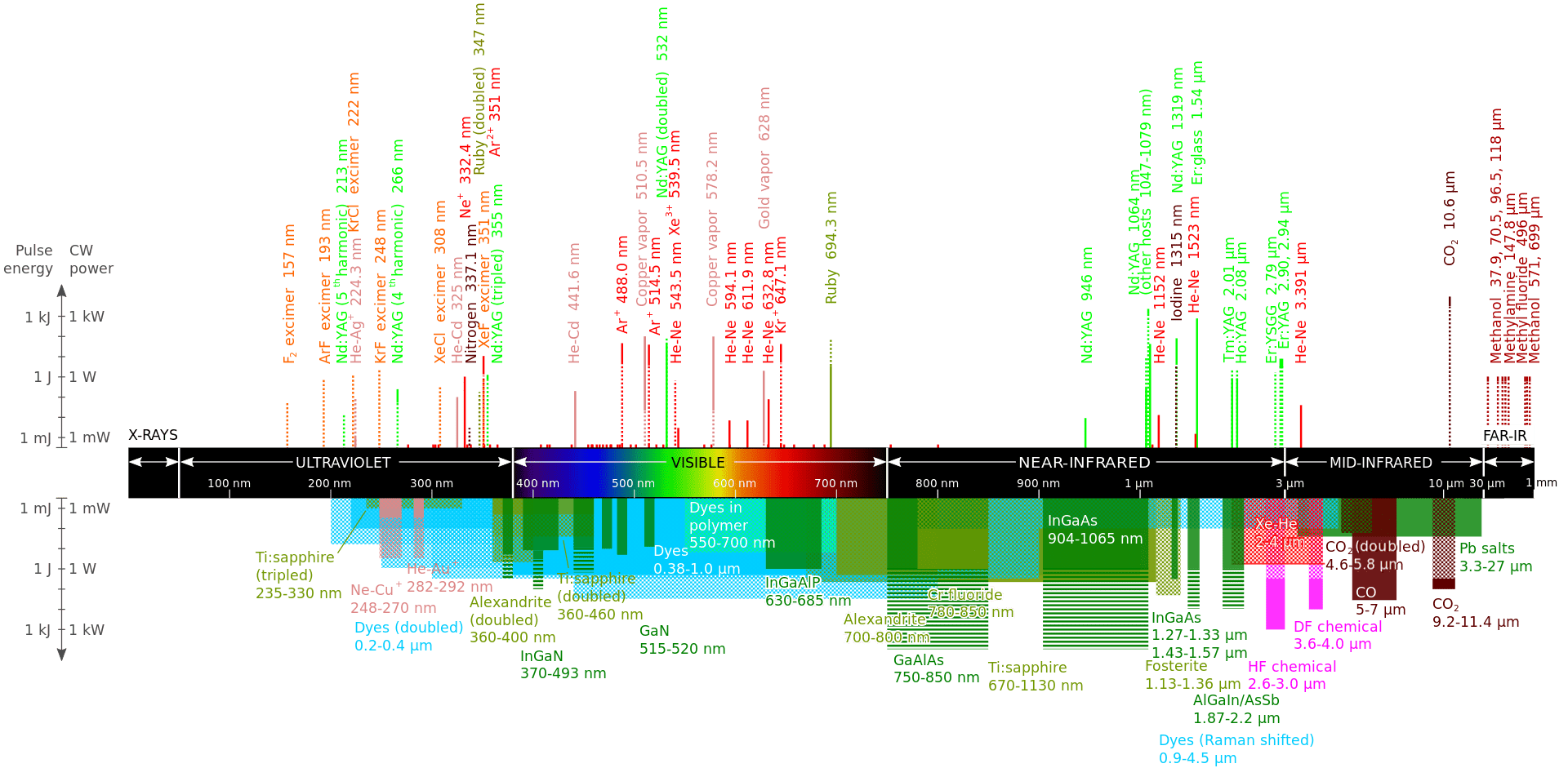
So far, the actual power of each chip of a blue semiconductor laser is about 5W at a single wavelength, so beam combining technology that combines the output of multiple chips is essential to obtain higher power output.
The first method is to use laser bar technology, which is to systematically generate a laser single chip (Single Emitter) on a wafer of semiconductor material. First, multiple individual laser chips are efficiently integrated into a so-called laser bar. Each laser bar can produce at least 50W of blue light. Then, through appropriate electrical connections, cooling and heat dissipation, and the use of special optical devices, multiple semiconductor laser bars are installed and combined into a semiconductor laser stack (Stack). The entire semiconductor laser can be composed of one or several semiconductor laser stacks. Currently, laser bar technology can reach 2kW blue light power.
Beam synthesis using semiconductor laser bar technology
The second method is to use semiconductor laser single tube (Single Emitter) technology, that is, each laser single tube is collimated with its own dedicated lens, so that the combined beam divergence can be kept as unchanged as possible and the beam divergence can be minimized. , thereby increasing the brightness of the laser. Current laser single-tube technology produces the best beam quality currently capable of reaching 1.5kW output power, which can be used in battery, electric vehicle and consumer electronics manufacturing.
Semiconductor laser single tube technology beam synthesis
Benefiting from the high efficiency and absorption rate of blue light with a variety of materials, consumer-grade laser engravers, such as LONGER RAY5 and B1 series, have been widely used in the processing of wood, metal, food, acrylic, ceramics and other materials.
Laser Engravers on Wood: For wood and wood-based materials, the blue laser engraver offers the best performance. The blue laser engraver has the efficiency of 20-25% and, based on the available research papers, blue 445-450nm wavelength has the absorption rate of 68% and 73% on pine wood and beech wood respectively. A CO2 laser engraver has an overall energy efficiency of 5% and its wavelength has the absorption rate of 85% and 88% on the same two materials. Hence, a blue laser engraver is approximately 3.4 times more efficient than a CO2 laser at the same power consumption.
Laser Engraving on Leather: Academic research has shown that the absorption rate of blue laser wavelength stands at 88% for a blue laser beam and approximately 38% for a 1.06µm infrared fiber laser beam. Hence, a blue laser engraver is approximately 2.3 times more efficient than a 1.06μm infrared laser at the same laser power, which guarantees that a blue laser engraver will perform better in leather engraving.
Laser Engraving on Food and Organic Materials: Fiber and CO2 lasers struggle with engraving food and the vast majority of organic materials. This is because food and organic materials have high water content, often as high as 70%. Water absorbs the majority of laser spectrum, however it transmits almost full blue laser beams as the absorption coefficient for water is 3*10^-4 cm-1 for 450nm laser. For 1.06µm wavelength, the absorption rate is 6000 cm-1, while for a 10.6µm CO2 laser beam the absorption even higher as it is 7000000 cm-1. This means that the practically all of a CO2 and fiber laser beams' power is spent on evaporating water, while a blue laser ignores water content and engraves on the actual organic material that need to be engraved, making the process much faster. In addition to that, plant species are very absorbent for blue laser beams.
Relevant data comes from the project of "Development of a multi-diode laser source technology based on diodes with wavelengths in the range of 350-550 nm, allowing modification of laser beam parameters to optimize cutting, engraving and sintering processes of materials used in industry.", which is co-financed by the European Union with funds from the European Regional Development Fund under the Intelligent Development Operational Program 2014-2020.